Family: Argidae
Family common name: argid sawflies
Subfamily: Sterictiphorinae
Genus: Aprosthema Konow, 1899
Subgenera: none
Argidae are found in all non-polar regions of the world (Smith and Middlekauff 1987Smith and Middlekauff 1987:
Smith DR and Middlekauff WW. 1987. Suborder Symphyta. In: Stehr FW ed. Immature Insects. Kendall/Hunt Publishing Company. Vol. 1: 754 pp., Smith 1992Smith 1992:
Smith DR. 1992. A synopsis of the sawflies (Hymenoptera: Symphyta) of America south of the United States: Argidae. Memoirs of the American Entomological Society 39: 1-201.). They are external foliage feeders with a wide range of host plants. Additionally, the family exhibits some uncommon behaviors like the excretion of defensive compounds and subsocialsubsocial:
Living in aggregations but lacking organizational structure as in true social insects; can describes insects with tendencies to protect or care for thier young, feed gregariously, and build cocoon masses.
habits (Smith 1992Smith 1992:
Smith DR. 1992. A synopsis of the sawflies (Hymenoptera: Symphyta) of America south of the United States: Argidae. Memoirs of the American Entomological Society 39: 1-201.).
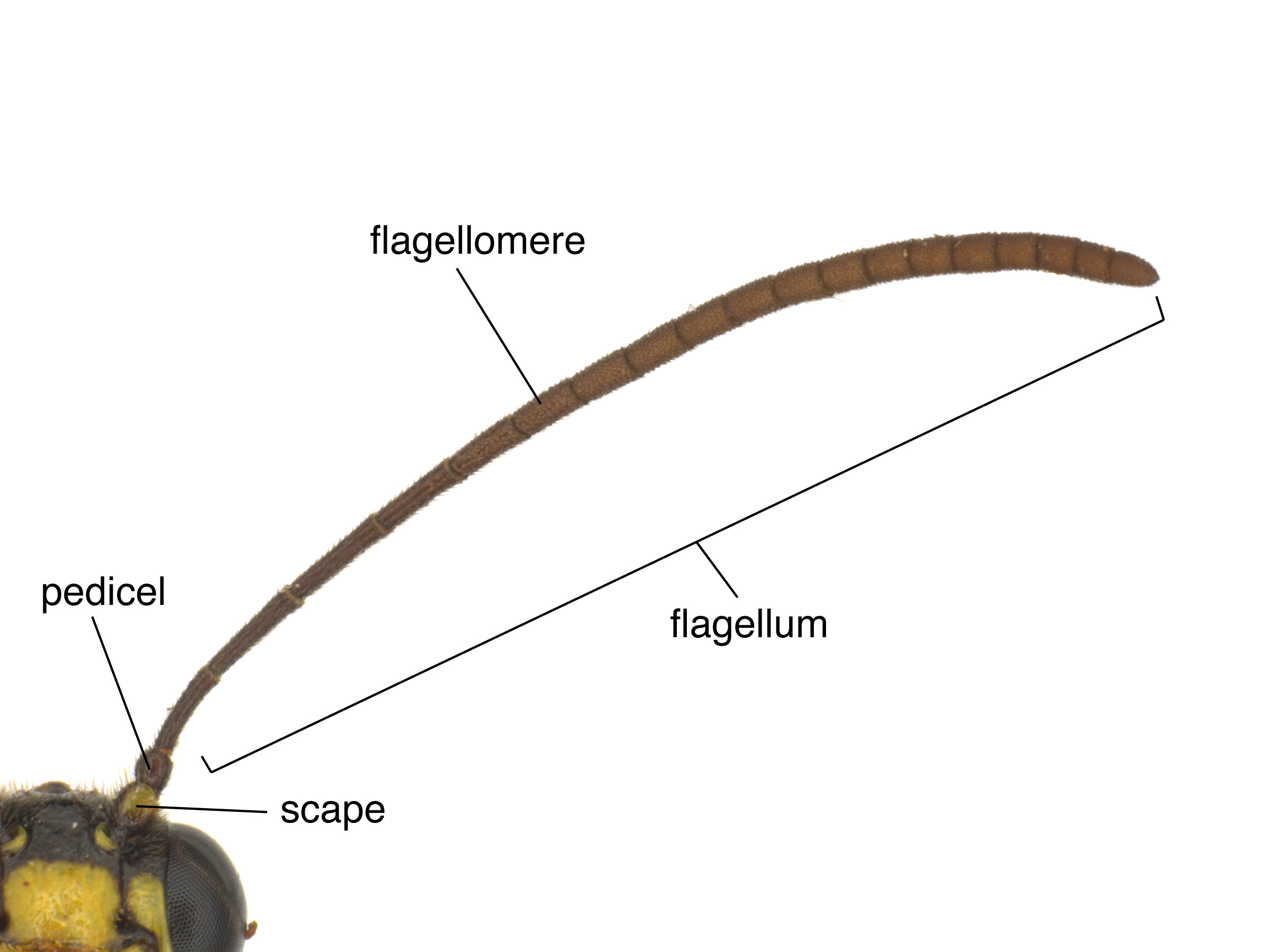
Aprosthema are rarely collected, and most species worldwide are described from a few or from a single specimen. They are recognized by characteristic 3-segmented antennaeantenna:
the sensory organ emerging from the front of the head, usually between the compound eyes and above the clypeus; includes the flagellum, scape and pedicel
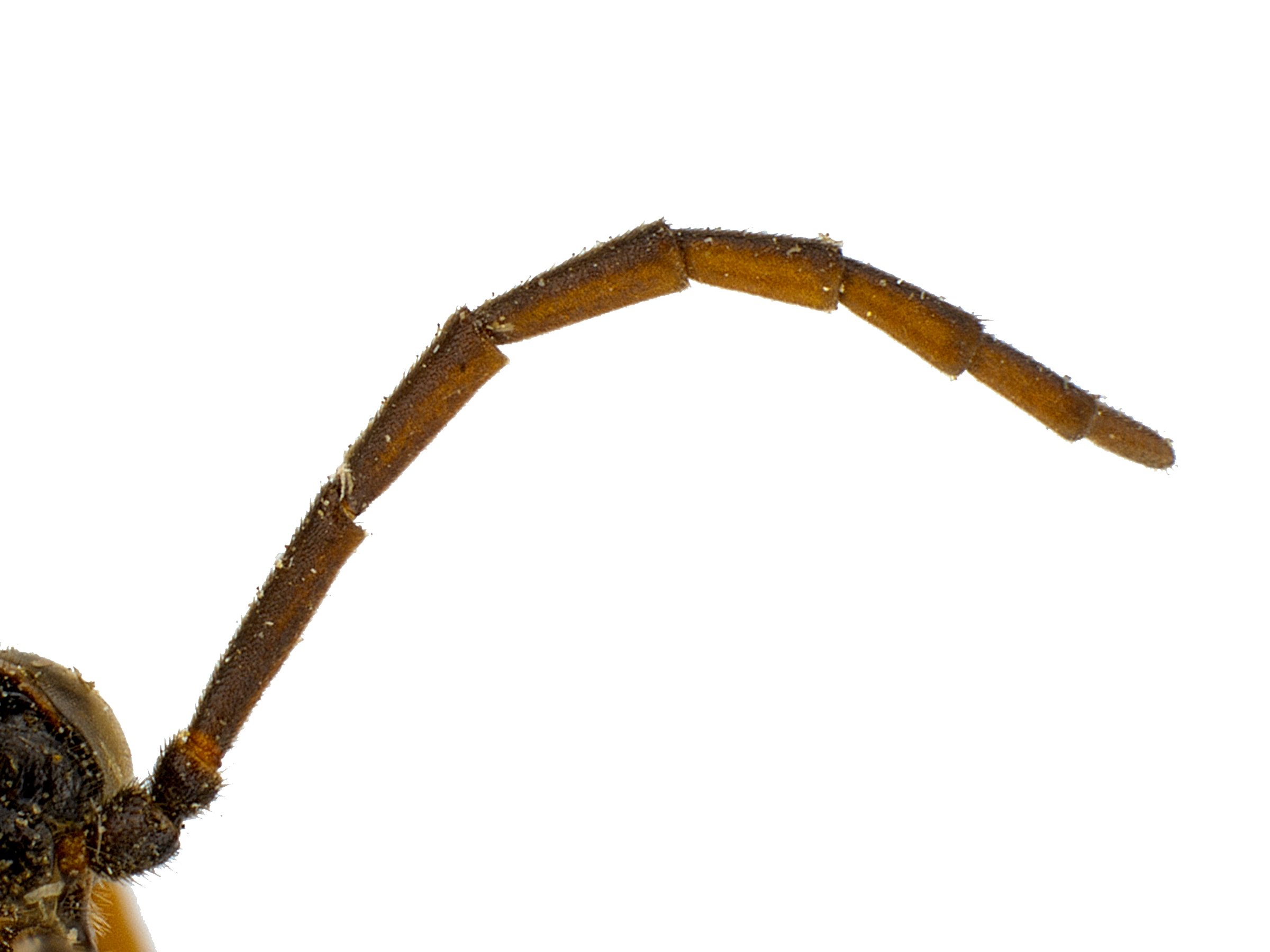 , which in males are distinctly forked (Smith 1971cSmith 1971c:
, which in males are distinctly forked (Smith 1971cSmith 1971c:
Smith DR. 1971c. Nearctic sawflies of the genera Neoptilia Ashmead, Schizocerella Forsius, Aprosthema Konow, and Sphacophilus Provancher (Hymenoptera: Argidae). Transactions of the American Entomological Society 97: 537-594., Vikberg 2004Vikberg 2004:
Vikberg V. 2004. Seasonal head dimorphism and taxonomy of some European species of Aprosthema (Hymenoptera: Symphyta: Argidae). Beitrauml;ge Zur Entomologie 54 (1): 107-125. https://doi.org/10.21248/contrib.entomol.54.1.107-125).
There are 57 described species restricted to the Northern Hemisphere. Species richness is relatively low in North America, with only two known species (Taeger et al. 2010Taeger et al. 2010:
Taeger A, Blank SM, and Liston AD. 2010. World Catalog of Symphyta (Hymenoptera). Zootaxa 2580: 1-1064.).
A key to North American species of Aprosthema is included in Smith 1971cSmith 1971c:
Smith DR. 1971c. Nearctic sawflies of the genera Neoptilia Ashmead, Schizocerella Forsius, Aprosthema Konow, and Sphacophilus Provancher (Hymenoptera: Argidae). Transactions of the American Entomological Society 97: 537-594..
 (Smith 1992Smith 1992:
(Smith 1992Smith 1992: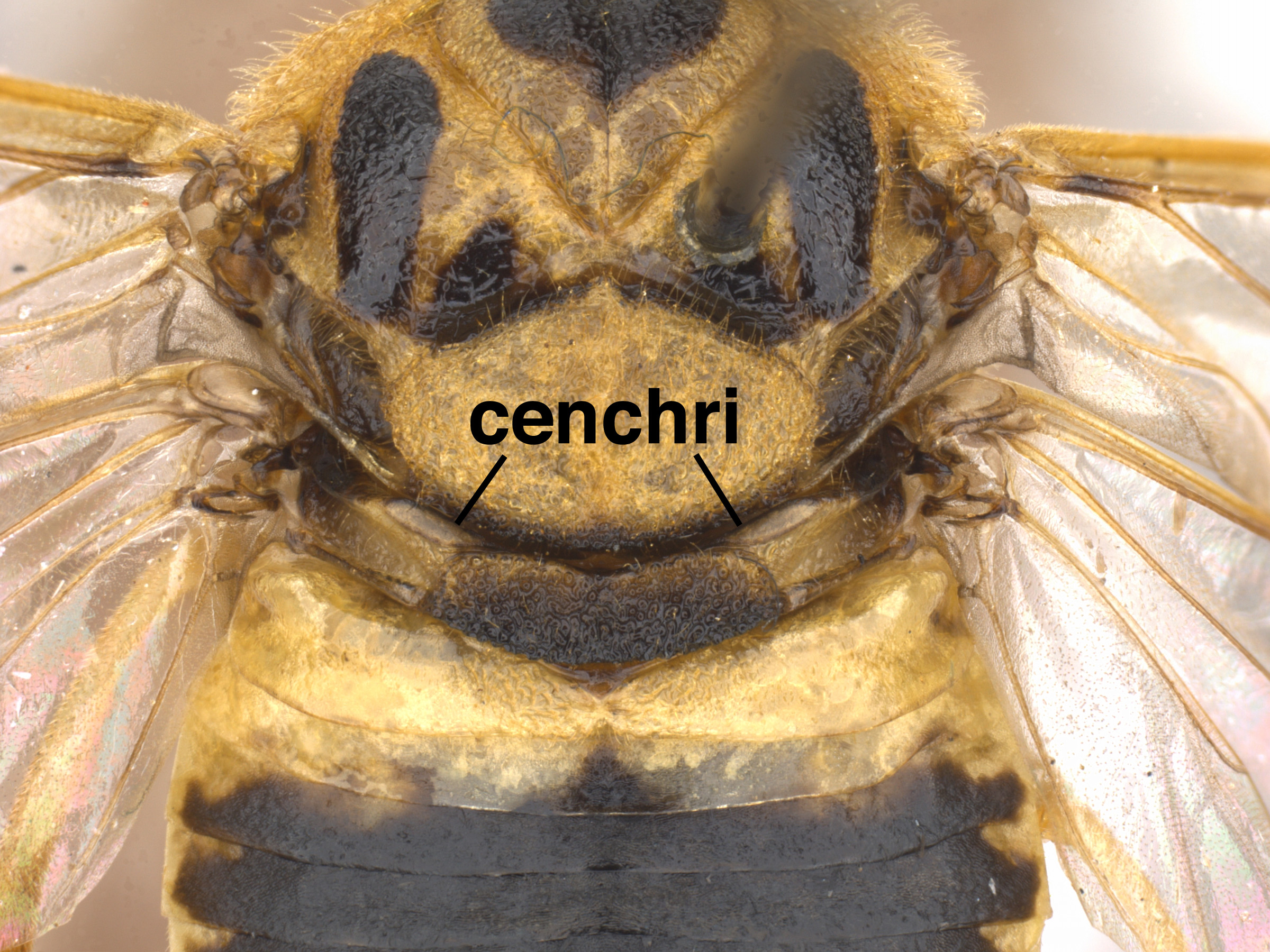 less than width of cenchruscenchrus:
less than width of cenchruscenchrus: (Smith 1992Smith 1992:
(Smith 1992Smith 1992: fused laterally with first tergitetergite:
fused laterally with first tergitetergite: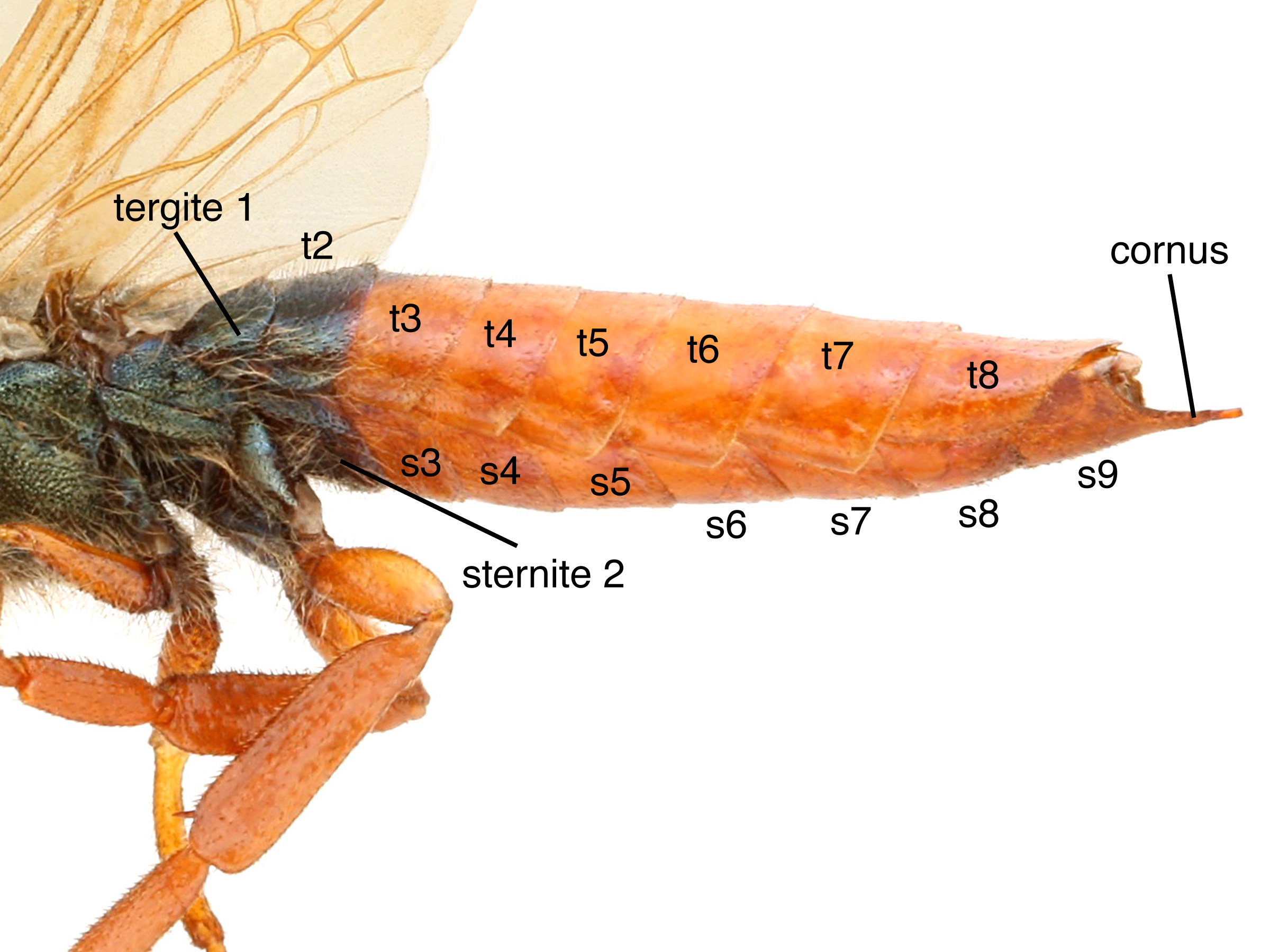 (Smith 1992Smith 1992:
(Smith 1992Smith 1992: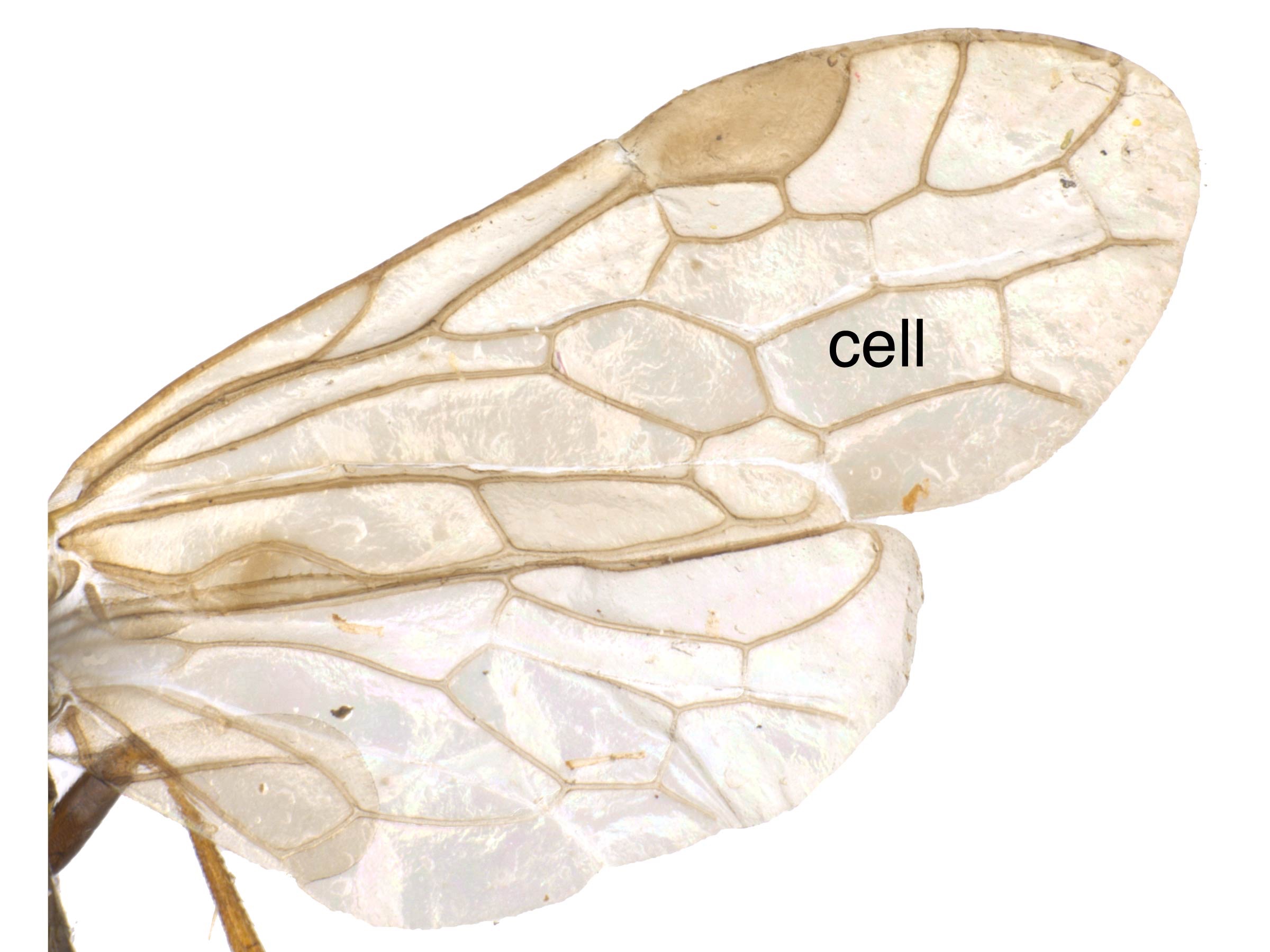 R open at apexapex:
R open at apexapex: (Smith 1992Smith 1992:
(Smith 1992Smith 1992: furcated; female antennaeantenna:
furcated; female antennaeantenna: clavate (Smith 1992Smith 1992:
clavate (Smith 1992Smith 1992:The family Argidae can be distinguished by the single-segmented flagellumflagellum:
the third section of the antennae that includes all the segments beyond the pedicel; segments of the flagellum are known as flagellomeres
 of the antennaantenna:
of the antennaantenna:
the sensory organ emerging from the front of the head, usually between the compound eyes and above the clypeus; includes the flagellum, scape and pedicel
 . The genus Aprosthema can be distinguished from other genera in the family by the lack of preapicalpreapical:
. The genus Aprosthema can be distinguished from other genera in the family by the lack of preapicalpreapical:
close to, but anterior to, the apex
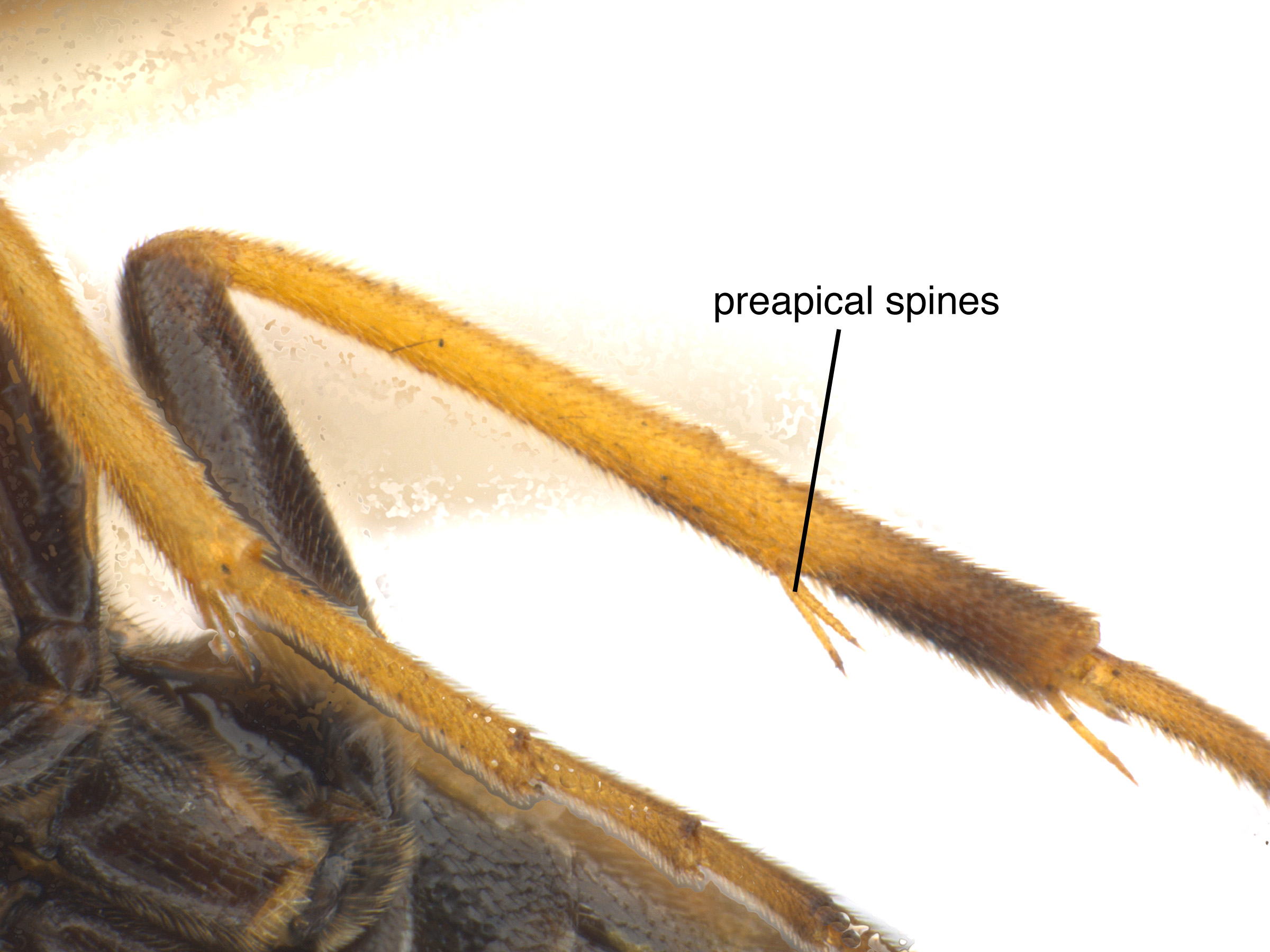 spurs on the tibiaetibia:
spurs on the tibiaetibia:
the fourth segment of the leg, between the femur and the tarsus
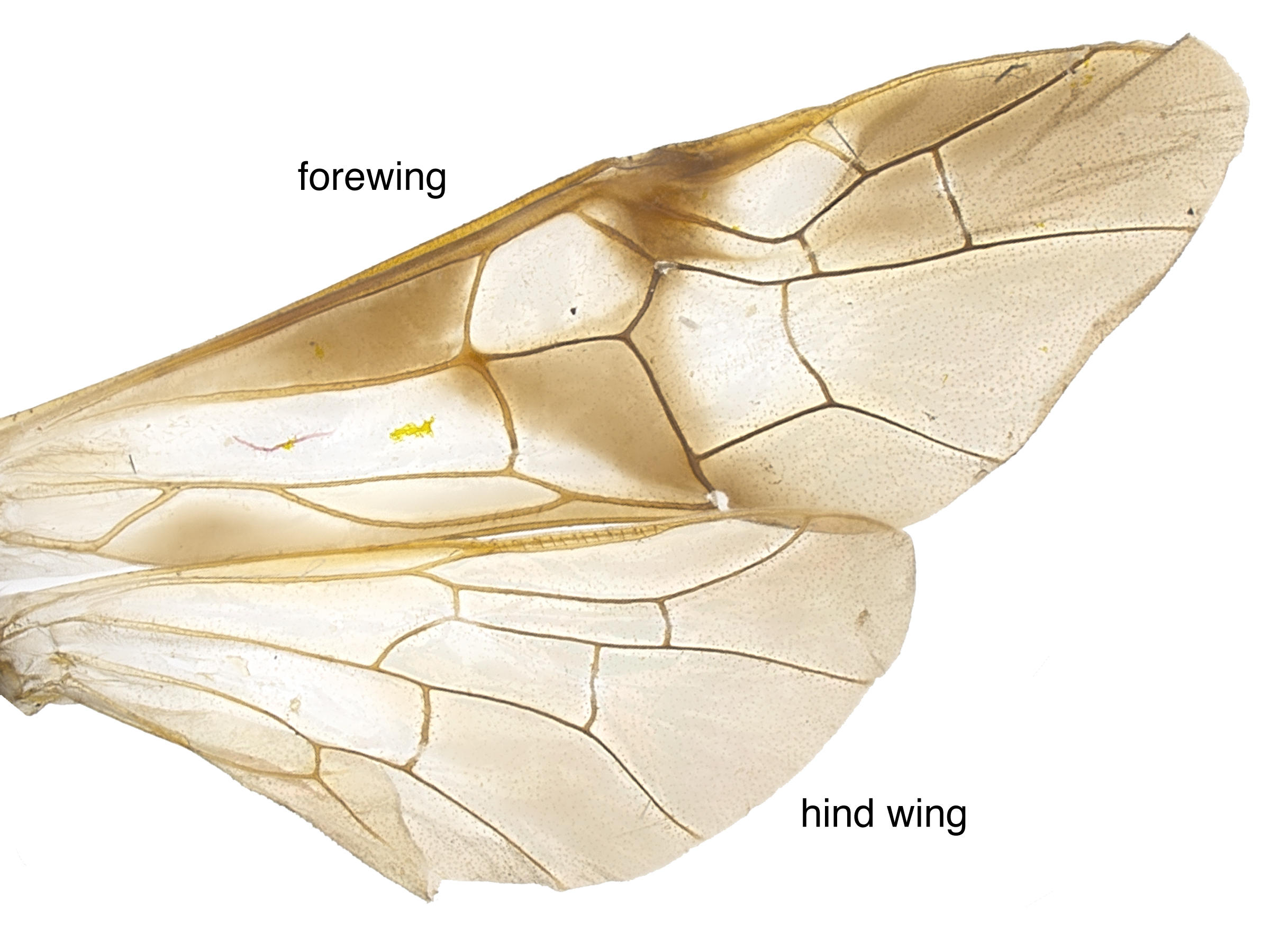
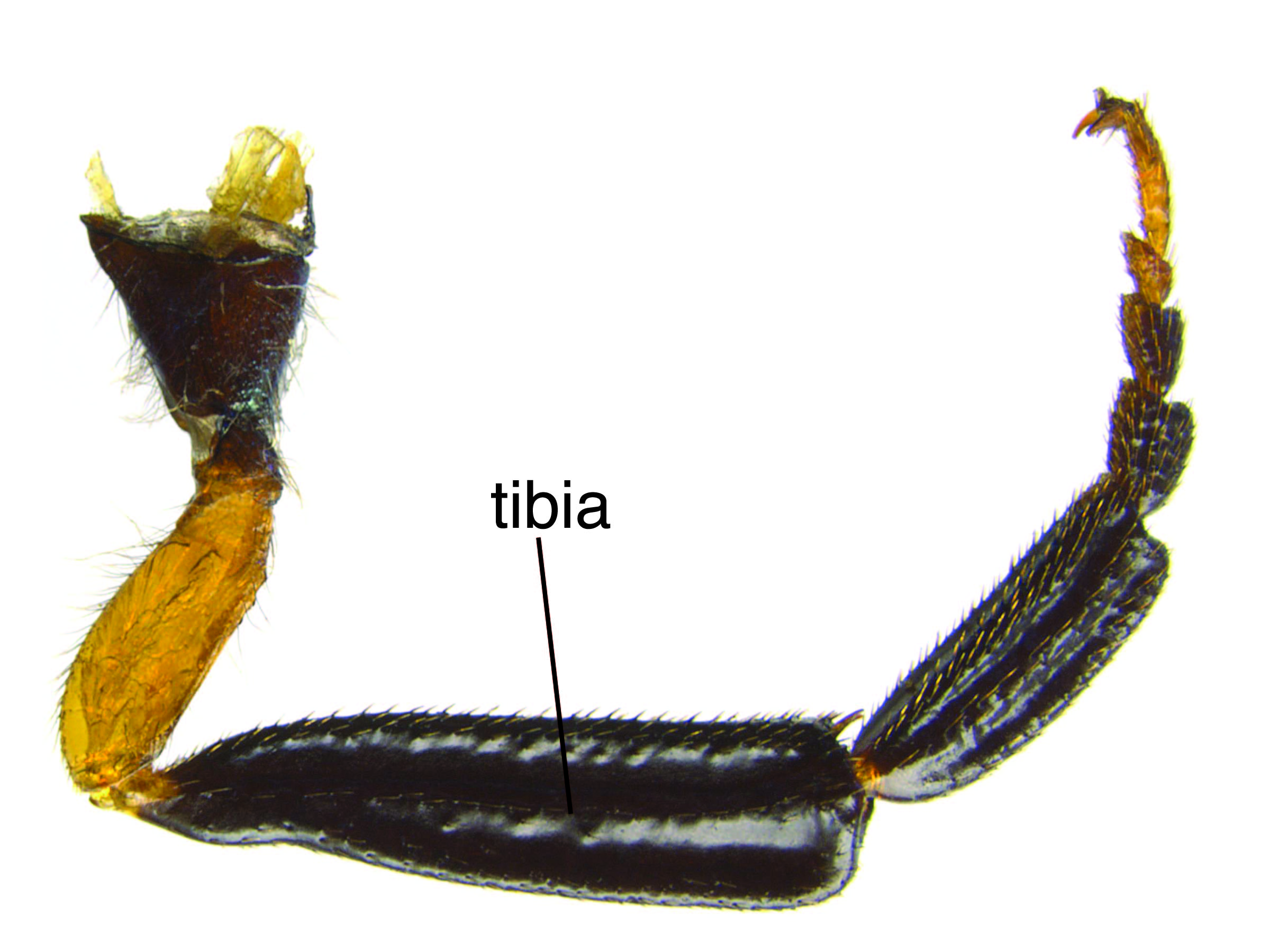 , simple tarsal claws, and a lack of veinvein:
, simple tarsal claws, and a lack of veinvein:
a tube-like, often darkened, structure on the wings
 Sc in the fore wingfore wing:
Sc in the fore wingfore wing:
the anterior wing of each pair of wings; usually the largest wing of the pair
 . Males are distinguished from related genera Arge and Atomacera by the conspicuous forked antennaeantenna:
. Males are distinguished from related genera Arge and Atomacera by the conspicuous forked antennaeantenna:
the sensory organ emerging from the front of the head, usually between the compound eyes and above the clypeus; includes the flagellum, scape and pedicel
 (Smith 1992Smith 1992:
(Smith 1992Smith 1992:
Smith DR. 1992. A synopsis of the sawflies (Hymenoptera: Symphyta) of America south of the United States: Argidae. Memoirs of the American Entomological Society 39: 1-201.).
none
Larvae are external leaf feeders, and in North America feed on species of Fabaceae, including Acmispon grandifloras (chaparral bird’s-foot trefoil), Hosackia sp., and Lotus sp. (Smith 1992Smith 1992:
Smith DR. 1992. A synopsis of the sawflies (Hymenoptera: Symphyta) of America south of the United States: Argidae. Memoirs of the American Entomological Society 39: 1-201.). Other leguminous hosts such as Vicia cracca (bird vetch) and Lathyrus vernus (spring vetchling) are recorded for European species of Aprosthema (Vikberg 2004Vikberg 2004:
Vikberg V. 2004. Seasonal head dimorphism and taxonomy of some European species of Aprosthema (Hymenoptera: Symphyta: Argidae). Beitrauml;ge Zur Entomologie 54 (1): 107-125. https://doi.org/10.21248/contrib.entomol.54.1.107-125).
Little is known about the biology of Aprosthema. In other genera of Argidae, the female oviposits along the margin of the leaf. After hatching, the larvaelarva:
the immature stage of holometabolous insects
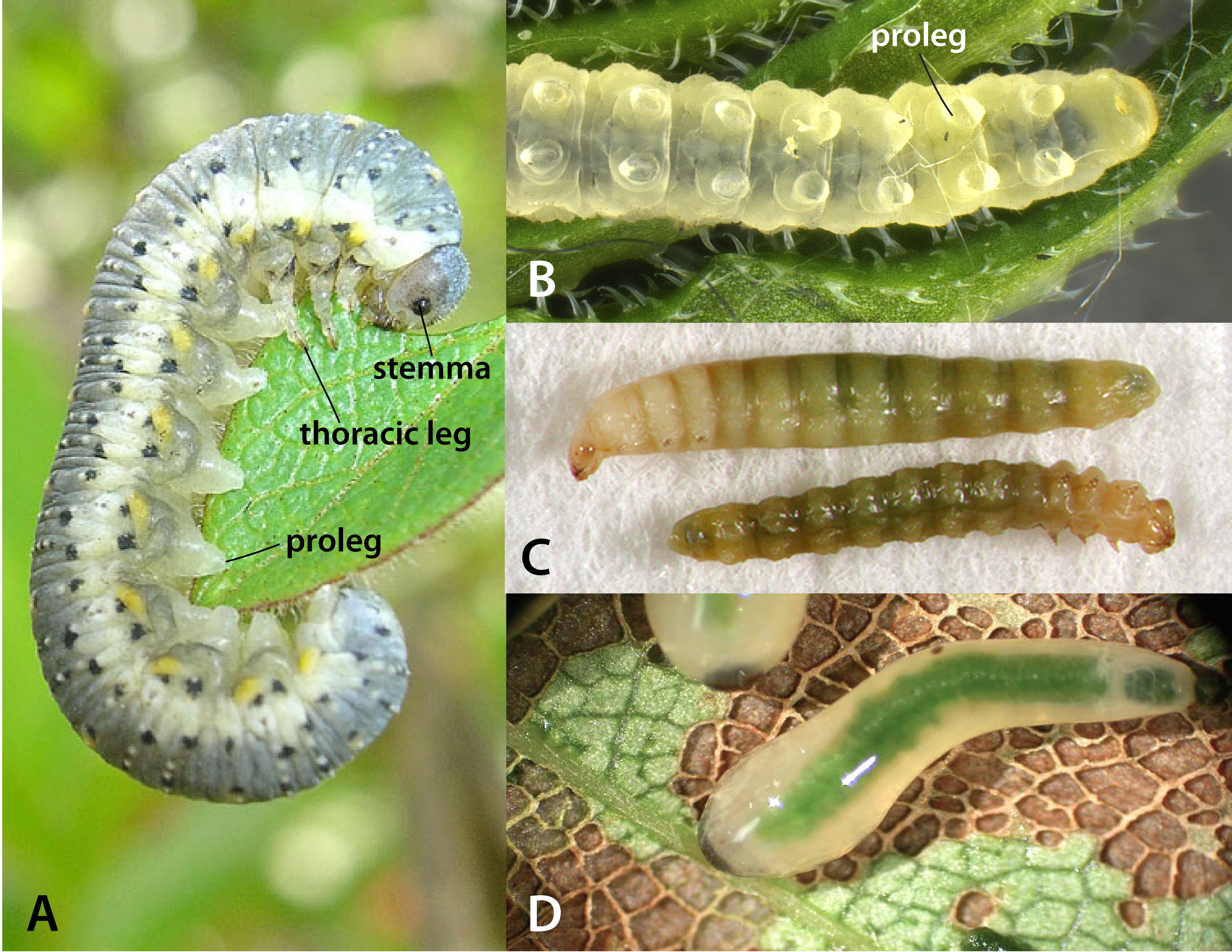 are external feeders on the foliage of plants (Smith 1989Smith 1989:
are external feeders on the foliage of plants (Smith 1989Smith 1989:
Smith DR. 1989. The sawfly genus Arge (Hymenoptera: Argidae) in the Western Hemisphere. Transactions of the American Entomological Society 115: 83-205.). Unlike other Argidae, larvaelarva:
the immature stage of holometabolous insects
 of the genera of the subfamily Sterictiphorinae are not known to live or pupate in aggregations (Smith 1992Smith 1992:
of the genera of the subfamily Sterictiphorinae are not known to live or pupate in aggregations (Smith 1992Smith 1992:
Smith DR. 1992. A synopsis of the sawflies (Hymenoptera: Symphyta) of America south of the United States: Argidae. Memoirs of the American Entomological Society 39: 1-201.).
World: This genus ranges throughout Europe, east into China and Russia, and in North America (Taeger et al. 2010Taeger et al. 2010:
Taeger A, Blank SM, and Liston AD. 2010. World Catalog of Symphyta (Hymenoptera). Zootaxa 2580: 1-1064.).
North America: Aprosthema is a western genus, with both North American species occurring in the Pacific Northwest (Washington, Oregon, California). Aprosthema brunniventre also occurs farther south into Nevada and Baja California Norte (Smith 1971cSmith 1971c:
Smith DR. 1971c. Nearctic sawflies of the genera Neoptilia Ashmead, Schizocerella Forsius, Aprosthema Konow, and Sphacophilus Provancher (Hymenoptera: Argidae). Transactions of the American Entomological Society 97: 537-594., Smith 1992Smith 1992:
Smith DR. 1992. A synopsis of the sawflies (Hymenoptera: Symphyta) of America south of the United States: Argidae. Memoirs of the American Entomological Society 39: 1-201., Taeger et al. 2010Taeger et al. 2010:
Taeger A, Blank SM, and Liston AD. 2010. World Catalog of Symphyta (Hymenoptera). Zootaxa 2580: 1-1064.).
Map data from: GBIF.org (26 June 2019) GBIF Occurrence Download Aprosthema
Details about data used for maps can be found here.